Part of speech
A part of speech is a category of words with similar grammatical properties.
Why should I understand part of speech?
Knowing parts of speech helps you talk and write better. It makes your sentences clear and organized.
It's like having tools to build strong and effective communication. So, understanding grammar basics makes you a better communicator!
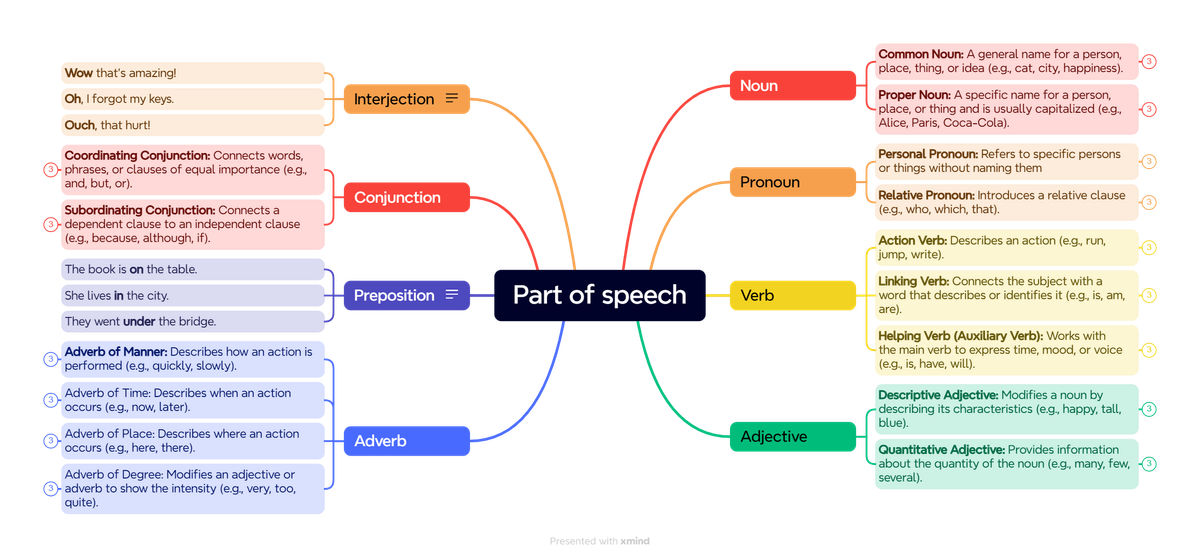
Noun:
Common Noun: A general name for a person, place, thing, or idea (e.g., cat, city, happiness).
- I saw a cat on the street.
- The city is bustling with activity.
- Happiness is a state of mind.
Proper Noun: A specific name for a person, place, or thing and is usually capitalized (e.g., Alice, Paris, Coca-Cola).
- Alice visited Paris last summer.
- I bought a bottle of Coca-Cola.
- Paris is known for its beautiful architecture.
Pronoun:
Personal Pronoun: Refers to specific persons or things without naming them (e.g., he, she, it, they).
- She is going to the party.
- They are my best friends.
- I saw him at the park.
Relative Pronoun: Introduces a relative clause (e.g., who, which, that).
- The book that I read was very interesting.
- The person who won the race received a trophy.
- I have a friend whose father is a doctor.
Verb:
Action Verb: Describes an action (e.g., run, jump, write).
- I love to run in the park.
- The dog jumped over the fence.
- She writes beautiful poems.
Linking Verb: Connects the subject with a word that describes or identifies it (e.g., is, am, are).
- She is happy.
- They are students.
- I am tired.
Helping Verb (Auxiliary Verb): Works with the main verb to express time, mood, or voice (e.g., is, have, will).
- I have finished my homework.
- She is going to the party.
- They will arrive soon.
Adjective:
Descriptive Adjective: Modifies a noun by describing its characteristics (e.g., happy, tall, blue).
- The sky is blue.
- He is a tall man.
- She has a beautiful smile.
Quantitative Adjective: Provides information about the quantity of the noun (e.g., many, few, several).
- I have many books on my shelf.
- There are few people in the park.
- She bought several apples from the market.
Adverb:
Adverb of Manner: Describes how an action is performed (e.g., quickly, slowly).
- She sings beautifully.
- He runs quickly.
- They danced gracefully.
Adverb of Time: Describes when an action occurs (e.g., now, later).
- I will see you tomorrow.
- She arrived late for the meeting.
- They left early in the morning.
Adverb of Place: Describes where an action occurs (e.g., here, there).
- He lives nearby.
- She went there for vacation.
- They met at the park.
Adverb of Degree: Modifies an adjective or adverb to show the intensity (e.g., very, too, quite).
- The movie was very interesting.
- He is too tired to go out.
- She is quite intelligent.
Preposition:
Shows the relationship between the noun (or pronoun) and other words in the sentence. It indicates location, direction, time, etc. (e.g., in, on, under).
- The book is on the table.
- She lives in the city.
- They went under the bridge.
Conjunction:
Coordinating Conjunction: Connects words, phrases, or clauses of equal importance (e.g., and, but, or).
- I like coffee and tea.
- He is tall but she is short.
- You can go by car or by train.
Subordinating Conjunction: Connects a dependent clause to an independent clause (e.g., because, although, if).
- I will go to the park if it stops raining.
- She couldn't sleep because it was too noisy.
- Although it was raining, they went for a walk.
Interjection:
An exclamatory word or phrase that conveys strong emotion or surprise (e.g., wow, oh, ouch).
- Wow, that's amazing!
- Oh, I forgot my keys.
- Ouch, that hurt!

